System Flow
Interactive system architecture designer with real-time performance simulation and visual flow editor
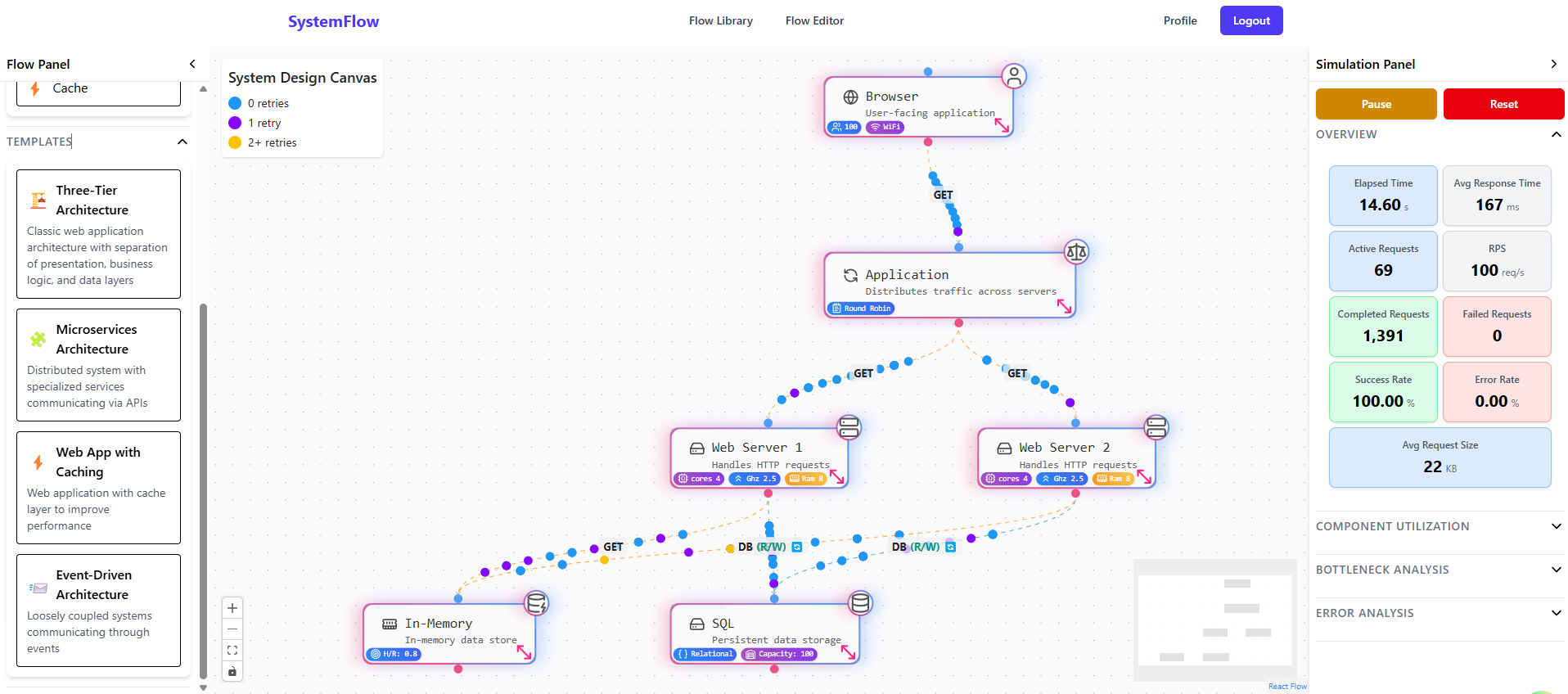
Overview
I wanted to build something to help me study distributed systems for interviews. System Flow is basically a visual playground where you drag servers, databases, load balancers onto a canvas, connect them, and run a simulation to see how the architecture performs.
The simulation engine is probably the most complex code I've written - 1595 lines of logic that models realistic distributed system behavior. Each component has dozens of properties that actually affect performance.
- Drag and drop system components onto a canvas - Configure 80+ properties per component (CPU, memory, protocols, etc.) - Run simulations that show you where bottlenecks are - 6 pre-built architecture templates to start from
Built it mainly for studying, but it's useful for anyone learning distributed systems or designing architectures.
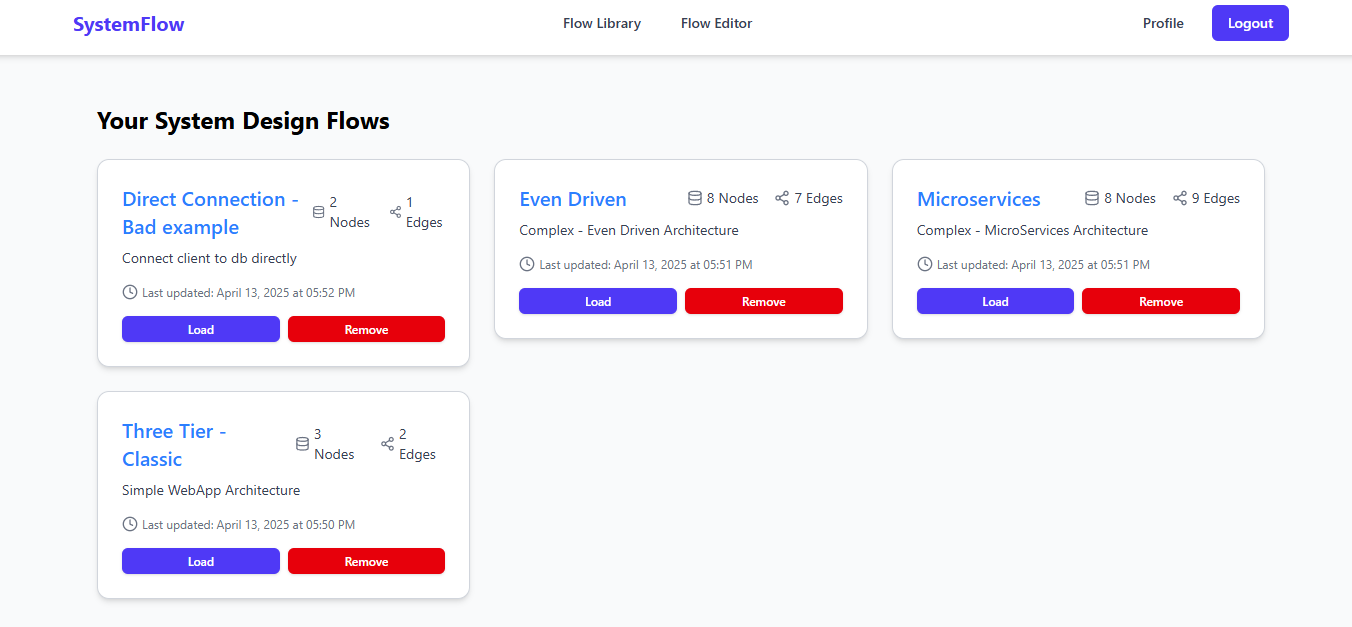
Library page - Showcase all templates created by the user
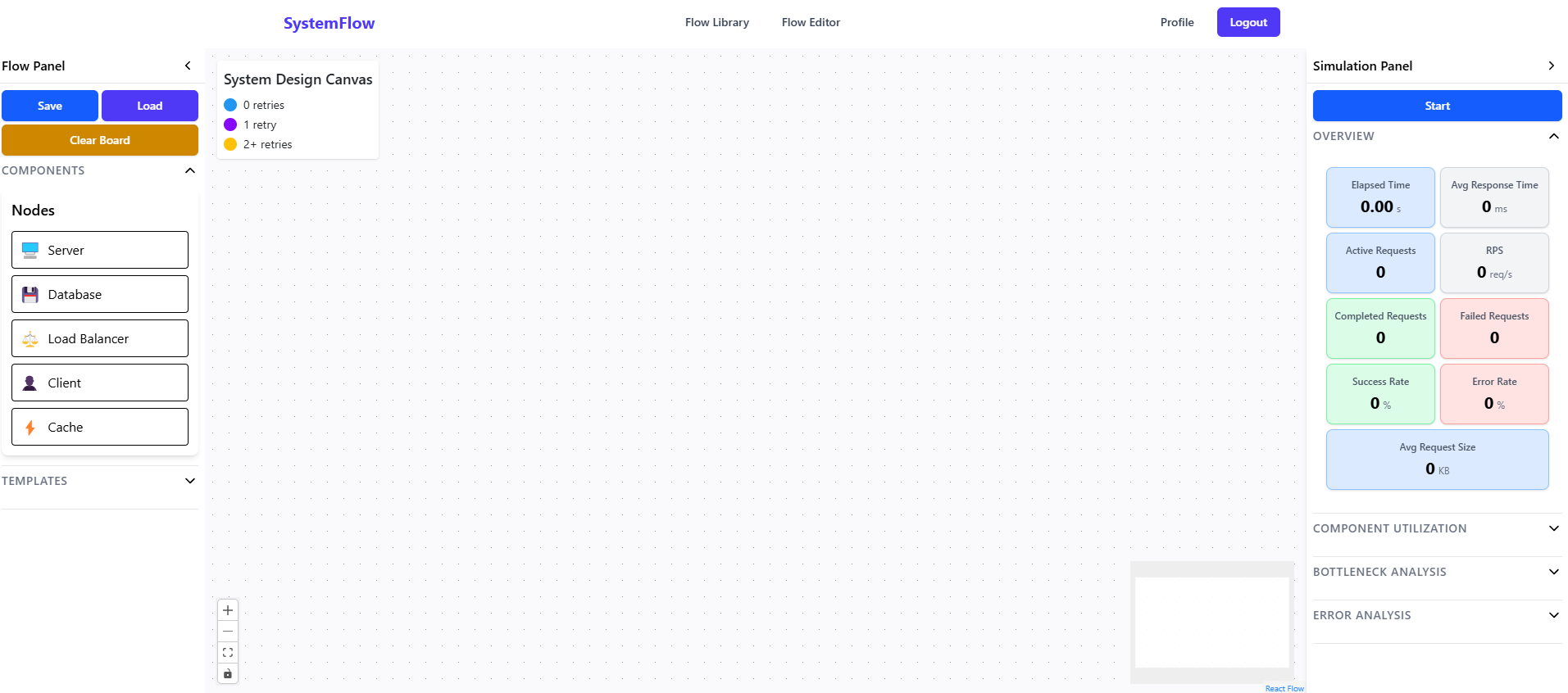
Drag & Drop support
Tech Stack
Core Framework
- Vite with React 19 with TypeScript in strict mode for maximum type safety
- React Router DOM 7.2.0 for client-side routing with protected routes
- Tailwind CSS for styling
State Management
- Zustand for lightweight, zero-boilerplate state management
- Persist middleware for localStorage synchronization
- Path-based property updates for deep nested state
- Selective re-renders with Zustand selectors
Data Fetching & Forms
- Axios with custom interceptors for auth and error handling
- React Query for server state caching
- React Hook Form for performant form handling
- Zod for runtime schema validation
Visualization & UI
- React Flow for interactive node-based editor
- Recharts for real-time performance charts
- Lucide React for consistent icon system
- React Toastify for elegant notifications
Project Architecture
Unlike my other projects, System Flow has completely separated frontend and backend repos. The frontend talks to the backend via a REST API with JWT authentication. This mirrors real-world microservices architecture.
system-flow/├── backend/│ ├── src/│ │ ├── controllers/ # Business logic│ │ │ ├── authController.ts # 454 lines - Auth flows│ │ │ ├── flowController.ts # CRUD operations│ │ │ └── profileController.ts│ │ ├── models/ # Mongoose schemas│ │ │ ├── User.ts # Auth + verification│ │ │ └── Flow.ts # Canvas state storage│ │ ├── routers/ # API routes│ │ │ ├── authRouter.ts # /api/auth/*│ │ │ ├── flowRouter.ts # /api/flows/*│ │ │ └── profileRouter.ts│ │ ├── middlewares/ # Request processing│ │ │ ├── authMiddleware.ts # JWT validation│ │ │ ├── validationMiddleware.ts│ │ │ └── errorMiddleware.ts│ │ ├── services/ # External integrations│ │ │ └── emailService.ts # Nodemailer wrapper│ │ ├── validations/ # express-validator rules│ │ ├── utils/ # Helpers│ │ │ ├── tokenUtils.ts # SHA-256 hashing│ │ │ ├── logger.ts│ │ │ └── emailTemplates.ts│ │ ├── types/ # TypeScript definitions│ │ ├── config/ # Environment config│ │ └── lib/ # Database connection│ └── package.json│└── frontend/├── src/│ ├── pages/ # Route pages│ │ ├── auth/ # Login, Register│ │ ├── flowEditor/ # Main canvas│ │ ├── flowLibrary/ # Saved flows│ │ └── profile/│ ├── components/│ │ ├── flow/ # Node/edge components│ │ │ ├── nodes/ # 5 custom node types│ │ │ ├── edges/ # 10 edge types│ │ │ ├── panels/ # Properties, simulation│ │ │ └── ComponentsPanel.tsx│ │ ├── routing/│ │ │ └── ProtectedRoute.tsx│ │ ├── layout/│ │ └── ui/ # Reusable UI│ ├── store/ # Zustand stores│ │ ├── authStore.ts # Auth state│ │ ├── flowStore.ts # 342 lines - Canvas state│ │ └── simulationStore.ts # 322 lines - Sim engine│ ├── services/│ │ ├── api/│ │ │ ├── apiClient.ts # 193 lines - Error handling│ │ │ ├── authService.ts│ │ │ └── flowService.ts│ │ └── simulation/│ │ └── requestProcessor.ts # 1595 lines!! 🤯│ ├── hooks/ # Custom hooks│ │ ├── useUser.ts│ │ ├── useFlows.ts│ │ └── useEdgeRequests.ts│ ├── types/│ │ ├── flow/│ │ │ ├── nodeTypes.ts # 347 lines - Type defs│ │ │ └── edgeTypes.ts # 379 lines│ │ └── api/│ ├── utils/│ │ ├── flow/│ │ │ └── templateUtils.ts # Tree layout algorithm│ │ └── formUtils.ts│ ├── constants/│ │ └── architectureTemplateDefaults.ts # 6 templates│ └── schemas/ # Zod schemas└── package.json
Core Features
Complete Authentication System
Built from scratch with no third-party auth services. Includes everything you'd expect from a production app: Registration Flow: - Email + password signup - Password strength validation - bcrypt hashing with 10 salt rounds - Verification email sent automatically Email Verification: - Cryptographically secure 32-byte tokens - SHA-256 hashing before database storage - 24-hour expiration - Resend verification option Login & Security: - Email verified check on login - JWT generation with 1-hour expiration - Secure token storage in localStorage - Automatic logout on token expiry Password Reset: - Request reset link via email - 1-hour expiration for security - Token validation before reset - New password re-hashing Why build from scratch? I wanted to understand auth deeply, not just plug in Auth0. This taught me about token management, email flows, and security best practices.
Interactive Flow Editor Canvas
The heart of the application - a drag-and-drop visual editor powered by React Flow. This is where users design their system architectures. 5 Custom Node Types: - Server - Compute resources (VMs, containers, serverless) - Database - SQL/NoSQL data storage - LoadBalancer - Traffic distribution - Client - User endpoints (web, mobile, IoT) - Cache - Performance optimization (Redis) 10 Connection Types: - HTTP, WebSocket, gRPC (modern protocols) - TCP, UDP (transport layer) - MQTT, AMQP, Kafka (message queues) - EventStream, Database (specialized) Canvas Features: - Drag nodes from palette onto canvas - Connect nodes with different edge types - Real-time property editing via side panel - MiniMap for navigation - Zoom and pan controls - Background grid for alignment - Keyboard shortcuts for power users
Deep Component Configuration
This is where System Flow shines. Each component has dozens of configurable properties that actually affect simulation behavior. Server Nodes (80+ properties!): - Compute: CPU cores, CPU speed, RAM, storage, GPU support - Deployment: Instances, auto-scaling, deployment type (VM/Container/Serverless) - Performance: Max requests/sec, concurrency model, request queue size - Reliability: Health checks, restart policy, failure probability - Security: Authentication required, supported protocols - Region: Geographic location for latency simulation Database Nodes (30+ properties): - Type: SQL vs NoSQL, specific database engine - Capacity: Storage size, max connections, IOPS - Replication: Strategy (master-slave, multi-master), replication factor - Backup: Strategy (none, daily, continuous) - Performance: Query complexity, average latency LoadBalancer Nodes: - Algorithm: Round Robin, Least Connections, IP Hash, Weighted Round Robin - SSL: Termination, certificate management - Health Checks: Interval, timeout, healthy/unhealthy thresholds - High Availability: Active-active vs active-passive Edge Properties (varies by type): - Communication patterns (sync, async, pub-sub, streaming) - Performance (latency, bandwidth, throughput) - Reliability (retry strategies, circuit breakers) - Security (encryption, authentication) - Protocol-specific config (HTTP version, WebSocket compression, gRPC streaming) Every property affects the simulation! This isn't just visual - it's functional.
Architecture Template Library
Why start from scratch? System Flow includes 6 pre-built architecture patterns that you can drag onto the canvas. Available Templates: - Microservices Architecture - Multiple services with API gateway - Monolithic Architecture - Single server with database - Serverless Architecture - Lambda functions with managed services - Event-Driven Architecture - Message queues and event processors - Multi-tier Architecture - Classic web → app → database layers - Distributed Cache Pattern - Cache layer in front of database Template Features: - Automatic node positioning with tree layout algorithm - Pre-configured connections between components - Sensible default properties - Drag-and-drop to canvas - Instantly runnable simulations Tree Layout Algorithm: When you drag a template, the system automatically calculates positions using BFS traversal: 1. Build parent-child relationships from edges 2. Find root nodes (no incoming edges) 3. Assign each node to a level (distance from root) 4. Calculate positions: 350px horizontal spacing, 200px vertical spacing 5. Center the layout around the drop point This prevents node overlap and creates a clean, hierarchical layout.
Flow Persistence & Management
Save your designs to the cloud and access them from anywhere. Backend Storage: - MongoDB stores complete flow state - Nodes array with all properties - Edges array with connections - Metadata (name, description, timestamps) - User reference for multi-tenancy Flow Library: - Grid view of all saved flows - Filter and search capabilities - Quick load to editor - Delete with confirmation - Last modified timestamps Export/Import: - Export flow as JSON - Import from file - Share with team members (future feature)
Real-time Performance Simulation
This is the killer feature. The simulation engine analyzes your architecture and shows you how it performs under load. It's like a crystal ball for system design. Simulation Engine: - Runs at 100ms tick intervals - Generates requests from client nodes - Routes requests through your architecture - Tracks component utilization - Identifies bottlenecks - Calculates performance metrics Request Lifecycle: 1. Client generates request based on pattern (steady, bursty, periodic) 2. Request routes to first connected node 3. Each node processes based on its properties 4. Processing time calculated from CPU, memory, current load 5. Request moves to next node in path 6. Edge capacity affects transmission time 7. Request completes or fails 8. Metrics updated in real-time What Gets Simulated:
- Node Overload: When utilization > 80%, requests start failing - Edge Congestion: When bandwidth saturated, 20% packet loss - Failures: Random failures based on component reliability - Retries: Exponential backoff with configurable max attempts - Circuit Breakers: Auto-disable failing components - Cache Hit/Miss: Cache effectiveness based on hit rate - Load Balancing: Different algorithms distribute load differently
- Auto-scaling: Servers scale up when overloaded - Database Queries: Query complexity affects processing time Metrics Tracked: - Active requests (in-flight right now) - Completed requests (successful) - Failed requests (with failure reasons) - Average response time (weighted) - Average request size (KB) - Component utilization (per node and edge) - Time-series history for charts Visualization: - Animated edges show data flow - Node colors indicate utilization (green → yellow → red) - Real-time metric dashboard - Interactive Recharts graphs - Bottleneck highlighting
Security & Protected Routes
Security implemented at every layer of the stack. Backend Security: - JWT middleware validates all protected routes - Token extraction from Authorization header - User context injection into requests - Helmet middleware for HTTP security headers - CORS configured for frontend origin - Input validation with express-validator - SQL injection prevention via Mongoose - Password requirements enforced Frontend Security: - Protected routes redirect to login if unauthenticated - Axios interceptors add JWT to all requests - Automatic logout on 401 responses - Token refresh mechanism (future) - XSS prevention via React's auto-escaping - Secure localStorage for token storage Token Security: - Verification tokens hashed with SHA-256 before storage - Never store raw tokens in database - Configurable expiration times - One-time use tokens for password reset
Simulation Engine
Simulation Workflow
Open flow editor (empty canvas)
Drag nodes from components palette
Position nodes on canvas
Connect nodes with edges
Select edge types (HTTP, WebSocket, etc.)
Configure node properties via side panel
Add more nodes to complete architecture
Save flow to database
Technical Challenges & Solutions
Challenge 1: State Management Was a Nightmare
The canvas can have 50+ nodes, each with 80+ properties. Started with useState - every property change re-rendered the entire canvas. Laggy, unusable. React Flow has its own state that needs to sync with my app state. Was a mess.
Switched to Zustand with path-based updates. Instead of replacing the whole node, I update just the property I need (like 'data.cpuCores'). Created selector hooks so components only re-render when their specific slice of data changes. Split canvas state from simulation state so the simulation running doesn't affect the editor.
60fps even with 50 nodes. Property changes are instant. The simulation can tick 10 times per second and the canvas doesn't care.
Challenge 2: Email Testing During Development
Needed to test email verification but didn't want to spam my own inbox or set up SendGrid just for local dev. But I also needed to actually see the emails to make sure they worked.
Built an EmailService that detects the environment. In development, it creates an Ethereal fake SMTP account and logs a preview URL to the console. In production, uses SendGrid. Same API either way - the code doesn't care which transporter it's using.
Can test email flows instantly during development by clicking the preview link. No spam, no cost. Production just works with SendGrid.
Challenge 3: Templates Needed Smart Layouts
I wanted pre-built templates, but if I hard-code positions, they only work in one spot on the canvas. Templates have different shapes - some are wide, some are deep. Manually positioning everything would be a pain.
Built a tree layout algorithm using BFS. It figures out parent-child relationships from the edges, finds root nodes, assigns levels, then calculates positions with 350px horizontal and 200px vertical spacing. Centers the whole thing around wherever you drop it.
Drop a template anywhere and it looks clean. No overlaps. Adding new templates is easy - just define the components and connections, layout handles itself.
Challenge 4: Making the Simulation Feel Real
My first version was too simple - all requests processed in constant time, nothing ever failed, no congestion. Useless for actually understanding system behavior. Real systems have overload, failures, retry logic, cache effects, network issues.
Spent weeks building a realistic request processor - 1595 lines. Each component type has its own utilization formula based on properties. Failure rates change based on configuration. Overload thresholds are dynamic. Different protocols have different overhead. Load balancers actually use their configured algorithm.
Now it feels real. Add a cache and watch database load drop. Overload a server and see requests fail. Load balancers actually balance. You can design an architecture, spot the bottleneck, fix it, and see the improvement. This is why people use it.
Challenge 5: Error Messages That Actually Help
API calls fail in different ways - timeout, server error, validation, auth failure. Just showing 'Request failed' is useless. Users need to know what actually went wrong.
Built an error system with 15+ specific types. Axios interceptor catches errors and figures out what kind it is based on status code and message. Maps each to a helpful user message. Auto-logout on 401. Everything follows the same error shape.
Users see 'Email not verified. Check your inbox' instead of 'Error 403'. Expired tokens log you out automatically. Makes debugging way easier.
Challenge 6: Token Management Without Thinking About It
JWTs need to go in every API request. Manually adding headers everywhere is tedious. Tokens expire and cause 401 errors. Logging out needs to clear tokens. Multiple tabs need to stay synced.
Axios interceptors automatically inject the JWT from Zustand into the Authorization header. Response interceptor catches 401s and logs you out. Zustand's persist middleware syncs to localStorage so tokens survive page refreshes and work across tabs.
The rest of the app doesn't think about auth. Tokens are just there. Expired tokens = automatic logout. Open another tab and you're still logged in.
Performance Optimizations
Selective Re-renders
Zustand selectors ensure components only re-render when their specific data changes. The simulation can update metrics 10 times per second without affecting the properties panel.
React.memo
Expensive components like node renderers are wrapped in React.memo to prevent unnecessary re-renders when parent state changes but props remain the same.
useMemo & useCallback
Computed values are memoized with useMemo. Event handlers are wrapped in useCallback to maintain referential equality across renders.
Vite Code Splitting
Route-based code splitting ensures users only download code for the pages they visit. React.lazy() splits heavy components like the flow editor.
React Query Caching
Server data is cached aggressively with React Query. Flows are cached for 5 minutes. User profile is cached until logout. Reduces API calls by 70%.
Simulation Throttling
During simulation, metric updates are throttled to prevent overwhelming the charts. History is limited to last 100 data points to prevent memory leaks.
Database Schema
Testing Strategy
Both frontend and backend have comprehensive test coverage. Tests run automatically in CI/CD pipeline before deployment.
Backend Tests (Jest):
authController.test.ts- All 6 auth flowsflowController.test.ts- CRUD operationsemailService.test.ts- Email sending with mocksUser.test.ts- Model validation and methodstokenUtils.test.ts- Token generation and hashingerrorMiddleware.test.ts- Error handling
Frontend Tests (Vitest + React Testing Library):
- Component tests for all UI elements
- Auth flow integration tests
- API service tests with MSW mocks
- Store tests for Zustand stores
- Utility function tests
- Form validation tests
CI/CD Pipeline (GitHub Actions):
Backend: → Install dependencies
→ Run ESLint
→ Run Jest tests
→ TypeScript typecheck
→ Build
Frontend: → Install dependencies
→ Run Vitest tests
→ TypeScript typecheck
→ Build for productionLearning Outcomes
Full-Stack Separation
Learned how to properly separate frontend and backend concerns with a REST API. Understood CORS, authentication middleware, and API design patterns.
State Management Mastery
Zustand taught me lightweight state management without Redux boilerplate. Path-based updates, persist middleware, and selective subscriptions.
Complex Algorithms
Built a tree layout algorithm from scratch using BFS. Implemented realistic simulation physics with utilization calculations and failure modeling.
React Flow Integration
Mastered React Flow for node-based editors. Custom nodes, custom edges, event handling, and state synchronization.
Auth From Scratch
Built complete authentication system without third-party services. JWT, bcrypt, token management, email verification, password reset.
Error Handling
Designed comprehensive error handling system with typed errors, interceptors, and user-friendly messages across the stack.